本文记述如何使用Kotlin实现一个PR四叉树(点-区域四叉树),并用该四叉树实现搜索给定区域中的点。
序言
四叉树和二叉树类似,都是树状结构。二叉树有两个子树,而四叉树有四个,这使得四叉树能够方便的对应上二维平面:将一个区域分割为四块,每块刚好对应一个子树。根据划分方式和存储的值的类型,四叉树有很多变体,例如区域四叉树(永远平均分割)、点四叉树(每次以某个点为中心进行区域分割)、点-区域四叉树(与区域二叉树类似,但叶节点存储其中的所有节点)、边四叉树等,关于四叉树的详细介绍这里就不多赘述了,想了解更多可以移步维基百科。
本文要实现的是点-区域四叉树。它在划分方式上与区域二叉树相同:永远在正中心将区域四等分。而它与区域二叉树不同的是,区域二叉树每个节点仅存储一个值,表示该区域的平均量;而点-区域二叉树在节点内存储所有包含在该片区域的点。因此很适合用来搜索给定区域中包含的所有点。
关于使用四叉树的好处这里就不多说了,因为很简单:如果不使用四叉树,要寻找位于指定区域内的点就需要顺序遍历所有点,而使用四叉树则可以直接排除掉部分点,因为这些子树所代表的区域与待查找区域没有交集,自然也没有符合条件的点。
模型定义
在实现四叉树之前,我们需要一些数据结构。处理二位平面就离不开坐标,为了保持通用性,我们将核心的坐标定义为一个接口XY:
interface XY {
val x: Int
val y: Int
}在本文中我们的操作对象仅限于点,因此实现一个点:
data class Point(
override val x: Int,
override val y: Int
) : XY然后我们还得想办法描述一个区域,关于区域的描述有很多种,比如:
- 给定中心点,分别给出半长和半宽
- 给定一个顶点,分别给出长和宽
- 给定两个顶点
本文选用第三种方法,直接给定两个顶点:
data class BoundingBox(
val topLeftX: Int,
val topLeftY: Int,
val bottomRightX: Int,
val bottomRightY: Int,
)而基于面向对象的方法,这个BoundingBox应当还有一些成员方法,例如判断一个点是否在其内部,是否与另一个区域相交,以及将自己划分为四个子区域:
data class BoundingBox(
val topLeftX: Int,
val topLeftY: Int,
val bottomRightX: Int,
val bottomRightY: Int,
) {
/**
* Test if a point is in the range of the box.
* Return true if the point is in the box.
*
* The top left corner is (0,0), the bottom right corner is (x,y).
* Also, the top left edges are included, but bottom right edges are excluded.
* */
fun containsPoint(point: XY): Boolean {
return point.x in (topLeftX until bottomRightX) && point.y in (topLeftY until bottomRightY)
}
/**
* Test if the target box overlaps with this box.
*
* By "overlap", there must be shared area, not shared edges.
* So just share the same edges doesn't mean overlap.
* */
fun overlap(target: BoundingBox): Boolean {
if (target.bottomRightX < this.topLeftX) {
// target on the left
return false
}
if (target.topLeftX > this.bottomRightX) {
// target on the right
return false
}
if (target.bottomRightY < this.topLeftY) {
// target on the top
return false
}
if (target.topLeftY > this.bottomRightY) {
// target on the bottom
return false
}
return true
}
/**
* Split this box and get 4 sub boxes.
* Index:
* + 0: top left
* + 1: top right
* + 2: bottom left
* + 3: bottom right
* */
fun getSubRegion(index: Int): BoundingBox {
val newBoxWidth = (this.bottomRightX - this.topLeftX) / 2
val newBoxHeight = (this.bottomRightY - this.topLeftY) / 2
return when (index) {
0 -> BoundingBox(
this.topLeftX, this.topLeftY,
this.topLeftX + newBoxWidth, this.topLeftY + newBoxHeight
)
1 -> BoundingBox(
this.topLeftX + newBoxWidth, this.topLeftY,
this.bottomRightX, this.topLeftY + newBoxHeight
)
2 -> BoundingBox(
this.topLeftX, this.topLeftY + newBoxHeight,
this.topLeftX + newBoxWidth, this.bottomRightY
)
3 -> BoundingBox(
this.topLeftX + newBoxWidth, this.topLeftY + newBoxHeight,
this.bottomRightX, this.bottomRightY
)
else -> throw IllegalArgumentException("The index must in range [0,3]")
}
}其中containsPoint判断区域中是否包含某个点,判断坐标就是了。而overlap则判断是否与另一个边界有重叠:排除四种不可能重叠的情况,那剩下的就是重叠了。最后getSubRegion根据序号0到3,分别对应四个子区域,这样设计是为了初始化四叉树节点设计的(直接遍历0到3,而不是设定4个枚举类型)。
铺垫好了数据结构,下面我们说一说四叉树怎么写。
四叉树实现
基本框架
首先是树的基本内容:
class QuadTree(
/**
* The region of this quad tree representing.
* */
val region: BoundingBox,
/**
* The max amount of elements can contain before this quad tree split.
* */
private val capacity: Int,
) {
private val points: MutableList<XY> = ArrayList(capacity)
/**
* Subtrees, order: [topLeft, topRight, bottomLeft, bottomRight]
* */
private var _subTrees: Array<QuadTree>? = null
val subTrees: List<QuadTree>
get() = _subTrees?.toList() ?: emptyList()
/**
* Insert a point into this node.
* */
fun insert(point: XY): Boolean {
TODO()
}
/**
* Return all points in the given range
* */
fun searchRange(target: BoundingBox): List<XY> {
TODO()
}
}
目前这个类包含了一些基本的成员,例如当前节点表示的区域、节点容量(在点过多时分裂节点)、点列表、子树列表。这里子树列表用的数组表示,最初为null,仅在需要时才分裂节点。但是当外部请求的时候,我们希望给的是不可变列表,从而避免调用者拿着返回值乱搞,所以将内部的成员起名为_subTrees,而subTrees则对应的是其不可变列表。
后面还定义了两个基本操作:插入(构建树)和查询。其中查询比较简单,我们先说说查询。
查询
查询功能将根据给定的区域,搜索以本节点为树根的四叉树中,所有位于给定区域中的点。这个还是很好实现的:
fun searchRange(target: BoundingBox): List<XY> {
if (!this.region.overlap(target)) {
// no overlaps, no points
return emptyList()
}
return this._subTrees
?.flatMap { it.searchRange(target) }
?: this.points.filter { target.containsPoint(it) }
}首先判断给定区域与当前区域是否有重叠——如果没有,那肯定查不到节点,直接返回空列表,这就相当于剪枝。之后根据当前节点的状态,有两种情况:
- 若子树为空,则本节点为叶子节点,存储了点信息
- 若子树不为空,则本节点已经分裂,不包含任何点信息
若子树不为空,则查找四棵子树,然后整理成不可变列表返回;否则搜索当前节点内的点。
插入
说完了查询,再说说插入。插入节点也可以分为两种情况:
- 若当前节点有子树,则直接插入子树节点
若当前节点没有子树
- 若节点未满,则存入点列表
- 若节点已满,分裂节点并插入子节点
其中插入子节点可以单独封装成一个方法:
private fun insertToSubRegions(point: XY): Boolean {
return this._subTrees?.any { it.insert(point) } ?: false
}若任意一个子树接受了点,则返回true,否则返回false。若没有子树,也返回false。这里利用了一个技巧来简化写法,即正常情况下,有且只有一个子树能够接受这个点(需要由当前节点保证该点在当前树枝的范围内),因此子树不为空时any总为true(有且只有一个子树插入成功,返回true),而我们想要的是它在判断true时尝试插入点,这样我们既插入了点,又得到了返回值。
之后即可按照上面的思路编写插入方法了:
fun insert(point: XY): Boolean {
if (!this.region.containsPoint(point)) {
// the point is not in this region, reject it
return false
}
if (insertToSubRegions(point)) {
return true
}
check(_subTrees == null) { "All 4 sub nodes rejected the point" }
return if (this.points.size < capacity) {
// now we can just insert and return
this.points.add(point)
true
} else {
// we need to split/subdivide this node into 4 sub nodes
_subTrees = Array(4) { QuadTree(region.getSubRegion(it), capacity) }
// empty the points and insert them in to sub nodes
points.forEach { check(insertToSubRegions(it)) { "Father node accepted, but all sub nodes rejected" } }
points.clear()
// try sub nodes
insertToSubRegions(point)
}
}在插入前检查范围,如果待插入的点根本不在当前树枝的覆盖范围内,则直接返回false。然后尝试插入子树:插入成功则返回true,插入失败则有两种情况,要么子树为空,要么全部子树拒绝了这个点。后面的check要求子树为空,否则直接抛出IllegalStateException,因为四棵子树必须有且只有一棵接受这个点。检查通过之后就可以确认子树是空的,因此可以先看节点容量,没满则插入点列表,返回true;满了则分裂节点:首先产生4棵子树,然后将现有的点插入子树并清空,最后将新的点插入子树。将现有点插入子树时要求必须插入成功,否则就会出现树根接受了点,而子树拒绝了点的情况。
在实际运行时,这些check可能会拖慢运行速度,但在开发过程中,验证这些条件有助于排错。否则程序无声无息的挂掉了,你都不知道从何处入手。
搜索可视化
写完了树,当然要用用看。既然是平面数据,自然离不开可视化。这里我们随机初始化一些点,然后随机给一个搜索区域,通过四叉树搜索区域中的点,并赋予不同颜色画出来。
package info.skyblond.quadtree
import java.awt.BasicStroke
import java.awt.Color
import java.awt.Graphics2D
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage
import java.awt.RenderingHints
import java.awt.geom.Ellipse2D
import java.io.File
import javax.imageio.ImageIO
import kotlin.random.Random
object QuadTreeDemo {
private const val width = 360
private const val height = 240
@JvmStatic
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val boundary = BoundingBox(0, 0, width, height)
val quadTree = QuadTree(boundary, 4)
val dots = (width.toDouble() * height * 0.02).toLong()
for (i in 1..dots) {
val p = Point(Random.nextInt(width), Random.nextInt(height))
quadTree.insert(p)
}
// 1 extra for edge stroke
val image = BufferedImage(width + 1, height + 1, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB)
val graphics = image.createGraphics()
graphics.background = Color.BLACK
graphics.color = Color.WHITE
// draw quad tree tiles
graphics.stroke = BasicStroke(1.0F)
drawQuadTreeTile(quadTree, graphics)
// draw all points
graphics.color = Color.GREEN
quadTree.searchRange(boundary)
.forEach {
fillCircle(it.x, it.y, 1.0, graphics)
}
// search region
val searchWidth = Random.nextInt(width / 2)
val searchX = Random.nextInt(searchWidth)
val searchHeight = Random.nextInt(width / 2)
val searchY = Random.nextInt(searchHeight)
val searchRegion = BoundingBox(searchX, searchY, searchX + searchWidth, searchY + searchHeight)
graphics.color = Color.YELLOW
drawRegion(searchRegion, graphics)
// draw searched points
graphics.color = Color.RED
quadTree.searchRange(searchRegion)
.forEach { fillCircle(it.x, it.y, 1.0, graphics) }
// done
graphics.dispose()
ImageIO.write(image, "png", File("quadtree_search.png"))
}
private fun drawQuadTreeTile(quadTree: QuadTree, graphics: Graphics2D) {
drawRegion(quadTree.region, graphics)
quadTree.subTrees.forEach { drawQuadTreeTile(it, graphics) }
}
private fun drawRegion(region: BoundingBox, graphics: Graphics2D) {
val regionWidth = region.bottomRightX - region.topLeftX
val regionHeight = region.bottomRightY - region.topLeftY
graphics.drawRect(region.topLeftX, region.topLeftY, regionWidth, regionHeight)
}
fun fillCircle(centerX: Int, centerY: Int, radius: Double, graphics: Graphics2D) {
// save the old value
val oldValue = graphics.getRenderingHint(RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING)
graphics.setRenderingHint(RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING, RenderingHints.VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON)
val shape = Ellipse2D.Double(centerX - radius, centerY - radius, 2 * radius, 2 * radius)
graphics.fill(shape)
// recover the old value
graphics.setRenderingHint(RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING, oldValue)
}
}
一次运行的结果如下所示:
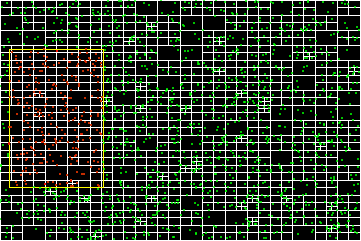
其中白框为四叉树各节点的覆盖范围,绿色点为普通点,黄色框为搜索框,红色点为四叉树搜索到的点。可见效果还是挺好的。
至于四叉树的性能嘛,如果只是寻找点的话,实际上它是比不过遍历列表的。因为遍历列表是循环,而查找树则是递归,除了保存栈帧等较慢的操作之外,还可能会出现栈内存溢出(点太多了,递归调用直接爆栈)。下一篇文章将介绍如何使用四叉树进行圆圈的碰撞检测,在这个过程中需要对每个圆搜索其附近的圆,如果使用列表的话,N个圆就是N^2次搜索,而使用树则近似为Nlog4 N,这时四叉树的优势就体现出来了。
四叉树完整代码
下面是四叉树的完整代码:
package info.skyblond.quadtree
class QuadTree(
/**
* The region of this quad tree representing.
* */
val region: BoundingBox,
/**
* The max amount of elements can contain before this quad tree split.
* */
private val capacity: Int,
) {
private val points: MutableList<XY> = ArrayList(capacity)
/**
* Subtrees, order: [topLeft, topRight, bottomLeft, bottomRight]
* */
private var _subTrees: Array<QuadTree>? = null
val subTrees: List<QuadTree>
get() = _subTrees?.toList() ?: emptyList()
/**
* Insert a point into this node.
* */
fun insert(point: XY): Boolean {
if (!this.region.containsPoint(point)) {
// the point is not in this region, reject it
return false
}
if (insertToSubRegions(point)) {
return true
}
check(_subTrees == null) { "All 4 sub nodes rejected the point" }
return if (this.points.size < capacity) {
// now we can just insert and return
this.points.add(point)
true
} else {
// we need to split/subdivide this node into 4 sub nodes
_subTrees = Array(4) { QuadTree(region.getSubRegion(it), capacity) }
// empty the points and insert them in to sub nodes
points.forEach { check(insertToSubRegions(it)) { "Father node accepted, but all sub nodes rejected" } }
points.clear()
// try sub nodes
insertToSubRegions(point)
}
}
/**
* Insert to subregions
* */
private fun insertToSubRegions(point: XY): Boolean {
return this._subTrees?.any { it.insert(point) } ?: false
}
/**
* Return all points in the given range
* */
fun searchRange(target: BoundingBox): List<XY> {
if (!this.region.overlap(target)) {
// no overlaps, no points
return emptyList()
}
return this._subTrees
?.flatMap { it.searchRange(target) }
?: this.points.filter { target.containsPoint(it) }
}
}-全文完-

【代码札记】Kotlin实现四叉树寻找区域内的点 由 天空 Blond 采用 知识共享 署名 - 非商业性使用 - 相同方式共享 4.0 国际 许可协议进行许可。
本许可协议授权之外的使用权限可以从 https://skyblond.info/about.html 处获得。